Fujitsu Laboratories Ltd. today announced the launch of three collaborative research projects with world-leading research institutions: one with RIKEN and the University of Tokyo, another with Osaka University, and the other with the Delft University of Technology, in the Netherlands (hereafter, TU Delft). To make practical quantum computing a reality, Fujitsu will conduct research on a number of the associated technology layers, from the device level to control systems, architecture and algorithms. Through this collaborative research, Fujitsu aims to achieve comprehensive and efficient advances in quantum computing. By applying quantum computing to various fields currently facing problems that are extremely difficult to solve, Fujitsu aims to provide even greater value to customers and contribute to a sustainable society going forward.
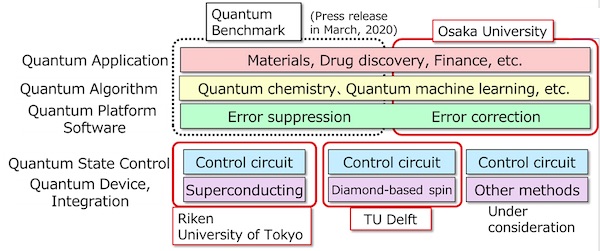
Figure: Technological Layers of Quantum Computing and Areas of Collaboration Background and Issues
Unlike conventional computers, which perform calculations based on values of either 0 or 1 represented as bits, the smallest unit of information, quantum computers can perform many parallel calculations at high speed by using qubits that can simultaneously handle both 0 and 1 states. Nevertheless, even systems using superconducting chips, which are leading the way in quantum computing, remain limited to about 50-qubit systems, making it difficult for them to perform useful calculations. In order to improve performance, various technological improvements are required at the hardware level; this includes such measures as augmenting the number of quantum bits, increasing the time that quantum bit information is held (coherent time), and improving control systems. In addition, experts anticipate technological innovations in the software field, including the development of algorithms that can make useful calculations even in a short coherent time.
Outline of the Joint Research
In order to make quantum computing more practical, Fujitsu will embark on new joint research initiatives with leading global research institutions, while strengthening medium- and long-term research efforts across all technological layers of quantum computing. By developing the technologies fostered through this collaborative research, Fujitsu aims to commercialize fault-tolerant quantum computing solutions in the future.
1. Research project with RIKEN and the University of Tokyo
Fujitsu will conduct research on superconducting quantum computers, which are currently regarded as the most promising type, with RIKEN and the University of Tokyo, both of which have strengths in superconducting qubit technology. Through a comprehensive undertaking of quantum computing systems covering quantum devices, and electronic control units and software, Fujitsu aims to bring about computer systems that can work in a complementarily fashion with conventional computers.2. Research project with TU Delft
Fujitsu will conduct fundamental research and development of quantum computers using diamond-based spin qubits with TU Delft, which has strengths in such qubit technology. Such qubits are formed at defects, which can be created by introducing impurity atoms into diamond. A diamond NV center(1) is an example of the defects. This method, where the qubit state can be accessed by light, may be suitable for achieving a large-scale system. This is due to the fact that gate-operations between distant qubits avoid cross-talk noise from other qubits, and the size of refrigeration units for cooling qubits is expected to be small because the quantum states of diamond-based spin qubits can be stable at higher temperatures than most competing platforms. In addition to the development of devices and control systems, the possibility of novel error-correction codes using a new qubit coupling topology will also be explored. The research will be conducted at QuTech, a leading Quantum Technology institute and cooperation of TU Delft and TNO (the Netherlands organization for applied scientific research).3. Research project with Osaka University
Research and development of quantum algorithms will be conducted with the Graduate School of Engineering Science at Osaka University, which is strong in the theoretical field of quantum computing. In addition to algorithms for applications, Fujitsu will conduct research on error-correction technologies needed to achieve fault-tolerant quantum computing.In addition to these R & D activities, Fujitsu also began collaborative research on quantum algorithms using error suppression technologies with Quantum Benchmark(2) in April 2020, with the aim of developing useful applications on small-scale quantum computers.
Future Plans
Fujitsu will work with these research institutions and others to promote research for achieving practical quantum computing over the medium to long term. The focus will be on solving societal problems by applying quantum computing to the fields of drug discovery, materials, and finance, as well as in various application fields with challenges that are difficult to solve with conventional computers.
(1) diamond NV (Nitrogen-Vacancy) center A defect consisting of a vacancy in the diamond lattice next to a nitrogen atom, where a carbon atom is typically found.
(2) Error suppression technologies with Quantum Benchmark “Fujitsu Laboratories and Quantum Benchmark Begin Joint Research on Algorithms with Error Suppression for Quantum Computing” (Press Release issued March 25, 2020)
3 mins read
Fujitsu Commences Joint Research with World-Leading Institutions for Innovations in Quantum Computing