Exclusive Coverage by Tarun Taunk, Chief Editor ITVoice
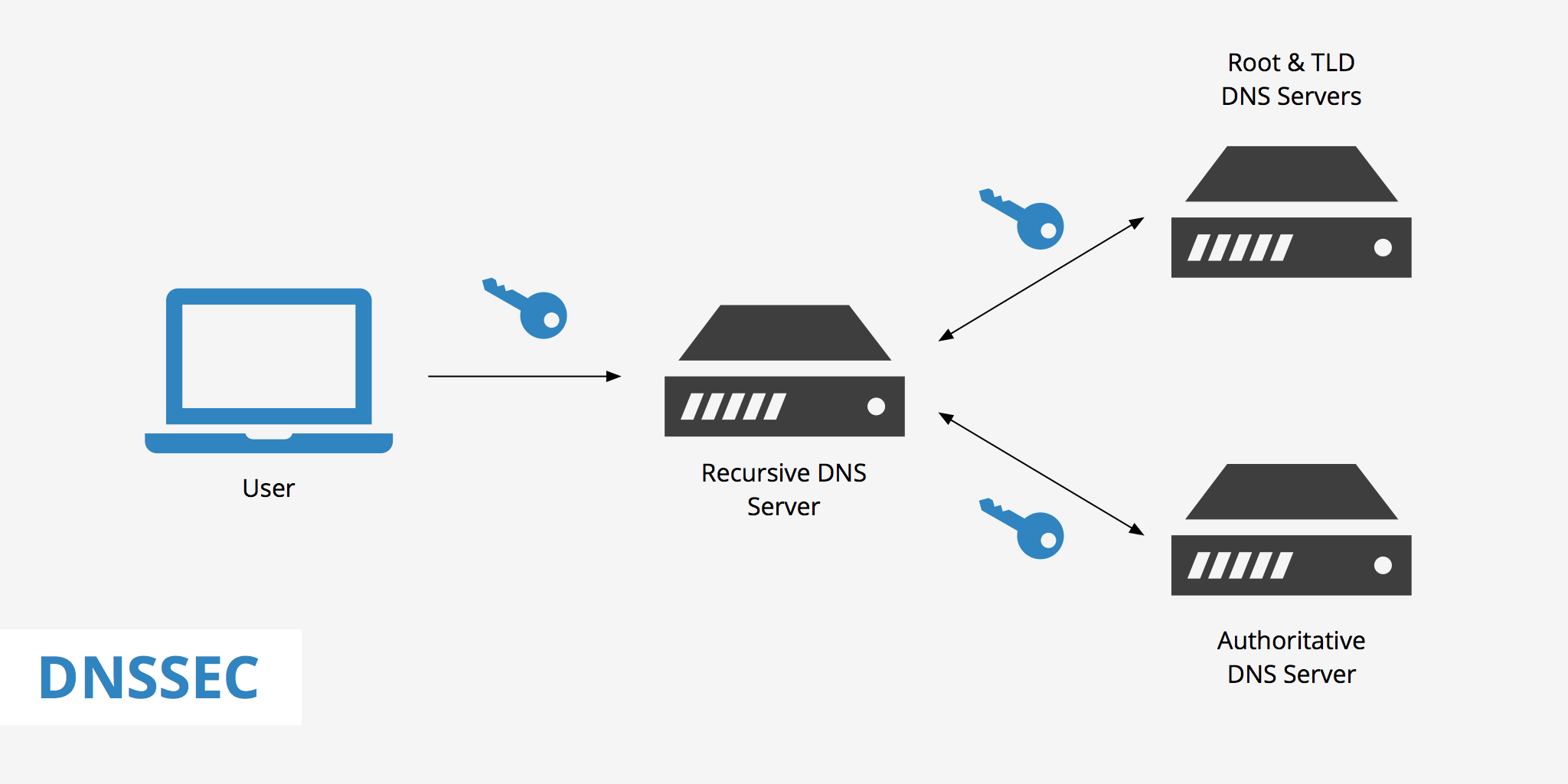
DNSSEC continues to be deployed around the world at an ever-accelerating pace. From the Root to both Generic Top Level Domains (gTLDs) and Country Code Top Level Domains (ccTLDs), the push is on to deploy DNSSEC to every corner of the internet. Businesses and ISPs are building their deployment plans too and interesting opportunities are opening up for all as the rollout continues. To make sure people know more about DNSSec this session was organized and presented by Ms Kathy Schintt.
She explained the below-mentioned topics in her presentation:
- Welcome and Introduction of DNSSec
- Basic Concepts of DNSSec
- Real World Examples
- Summary
To learn more about DNSSec or to know what Ms Kathy Schnitt explained in her presentaion read the article below.
DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC) are the upgrade for standard DNS protocol which initiates your internet surfing by locating domain names and mapping them to concerned IP addresses. DNS, at its base level, doesn’t deal with web vulnerabilities and therefore incurred several network-based issues with increasing popularity and user base. Subsequently, the need for secure systems cropped up, leading to the development of DNSSEC extensions that could be added to the existing DNS protocols to actuate secure browsing.
DNSSEC is designed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) as a set of extensions to protect users from cyber threats while navigating the web. DNSSEC adds authentication to the standard DNS system to make it more secure and invulnerable to popular cyber threats. DNSSEC implementation acts as an added layer of security to the domain name system which is now the universal standard for accessing web addresses across the globe.
Why do we need DNSSEC?
DNSSEC efficiently protects users from landing on deceitful websites or fraudulent addresses which may be targeted to harm users via network-based attacks. Unlike standard DNS, this system protects users from threats like poisoning, pharming, and man-in-the-middle attacks, thereby making the web experience much safer and effective. DNSSEC validates IP address resolution using cryptographic signature. Users never have to worry about the unintended website or pop-ups appearing on their screen while navigating through the web in search of their desired information.

How does it help with security?
DNSSEC follows advanced cryptographic signature validation to ensure users only land up on their desired addresses. The system digitally tags/ signs all the data requests which are directed to DNS servers in order to authenticate requests and resolve the exact address. Security validation in DNSSEC is powered by PKI authentication (public key infrastructure) which uses a couple of cryptographic keys (public and private) on each end. A private key is used to tag the DNS record and this signature is published in a system called Resource Record Digital Signature (RRSIG). This is an advanced level cryptographic technique used to secure modern-day digital protocol to actuate impenetrable security.
Session Leader: Kathy Schnitt
Staff Facilitator: Kathy Schnitt