The internet is being completely overtaken by OpenAI’s ChatGPT. On the official website of OpenAI, the AI-powered chatbot is available for public testing, and users may practically test out its functions for free. Many even claim that because ChatGPT’s responses are more conversational and human-like, it has a great deal of potential to replace Google Search. Furthermore, ChatGPT can even examine and produce programmes in a matter of seconds, which is bad news for aspiring programmers. Even challenging math issues can be resolved using it. Like other technologies, ChatGPT has its shortcomings, which the business has acknowledged.
What’s ChatGPT?
Simply put, ChatGPT is a chatbot where users can ask questions, and the platform uses artificial intelligence (AI) to provide replies. The company has created it so that users can receive both technical and non-jargony responses.
If you were to ask the chatbot to define simply and technically as to how exactly does it function, its response would be something like this for the technical answer. “ChatGPT is a natural language processing (NLP) model developed by OpenAI. It is a transformer-based model that is trained on a large corpus of conversational data. It is designed to generate human-like responses to user input, allowing for natural conversations with a virtual assistant.”
As for the simple answer, it would get back to your query with “ChatGPT works by using a large corpus of conversational data to train a transformer-based model. This model is then used to generate human-like responses to user input, allowing for natural conversations with a virtual assistant.”
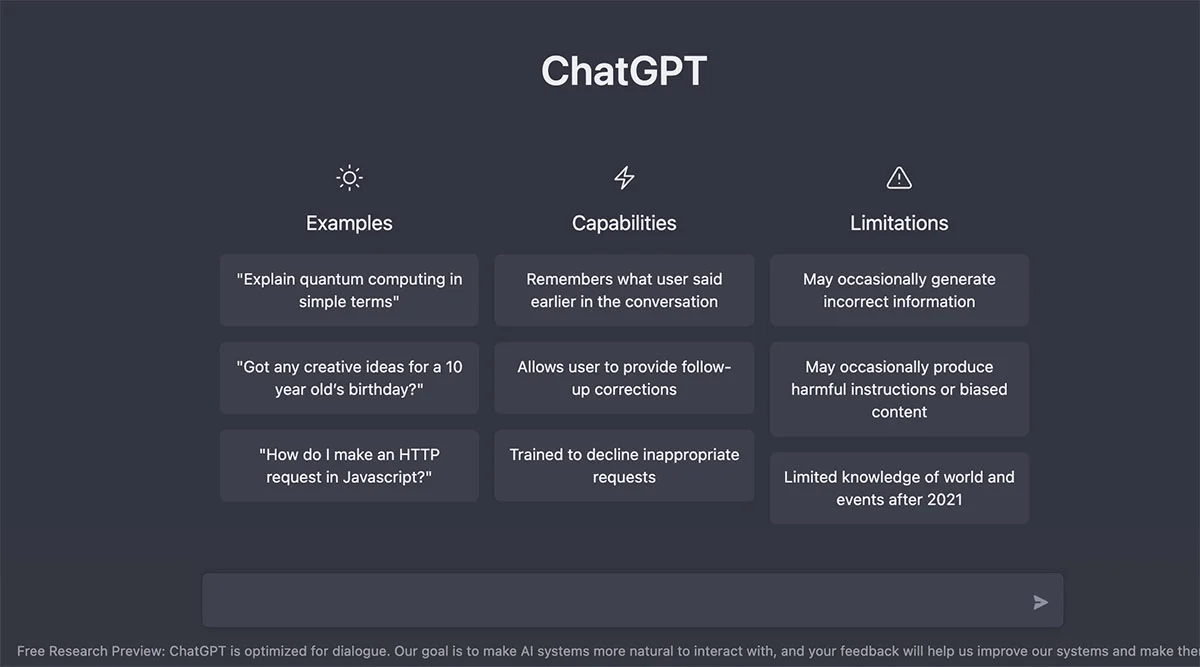
The chatbot employs Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) technology, according to the business, but has been modified to sound friendlier to people. It is built on GPT-3.5, a language model for deep learning that generates text that resembles human speech. If consumers ask the same question again in the future, they can receive different answers. That’s because the chatbot will develop over time and use machine learning to better interpret requests.
After the tests are finished, OpenAI can make ChatGPT’s underlying technology available to businesses that use chatbots. As an illustration, the chatbot can be utilised for students, personal assistants (to aid users with duties like scheduling, reminders, and other everyday activities), and customer service (for Airtel, Paytm, Swiggy, and more) (to help them solve complex questions in simple words).
Does this mean the end of Google Search?
According to OpenAI, ChatGPT’s expertise is restricted to world events that occurred before 2021 and will occasionally produce inaccurate information. There is a chance that it will “on occasion provide harmful instructions or biassed content.”
On Twitter, there are numerous posts that highlight its strengths. Similar to that, many have also noted its shortcomings. For instance, the chatbot struggled when we asked queries about specific nations.
If you were to ask if a particular mobile device like the iPad Pro 2022 can access 5G services on Airtel’s network, the AI bot’s answer would go something like this, “I am unable to browse the internet and therefore cannot provide information on whether the iPad Pro 2020 supports Airtel eSIM or not. My training data only goes up until 2021, so even if I could browse the internet, I may not have the most up-to-date information on this topic.”
This just goes on to show the current state of affairs of the chatbot and demonstrates how the Google search continues to be the staple source of information needed by billions of users on a day-to-day basis for generic queries.